Start building with us today.
Building a Geospatial Data Warehouse with PostgreSQL & PostGIS
Engineering the Geospatial Data Warehouse: A Comprehensive Course on PostGIS and PostgreSQL 17
1. Course Details
--Why This Course?
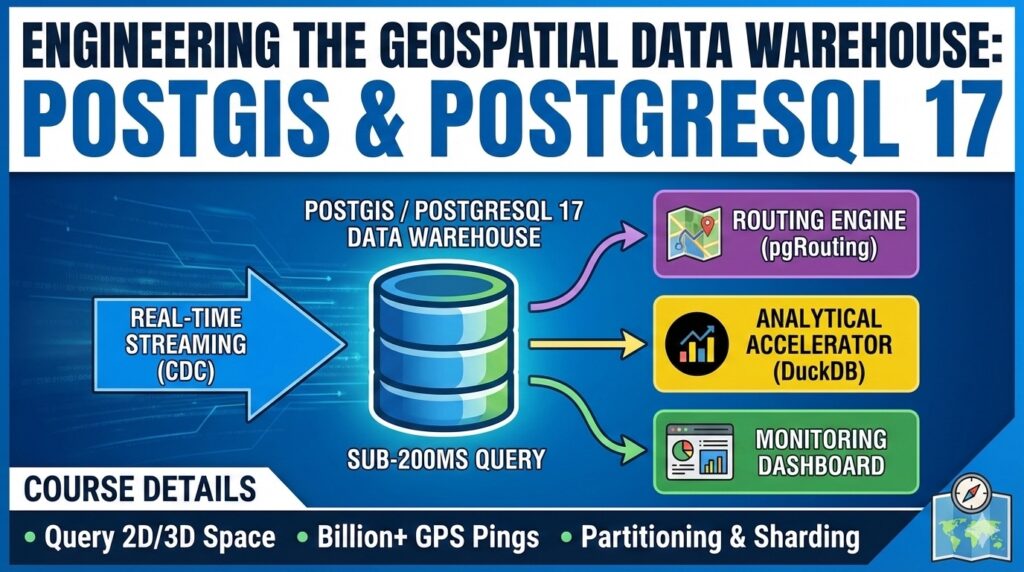
In modern software architecture, the ability to query 2D and 3D space with sub-200ms latency is a competitive necessity. Standard database courses often ignore the specific challenges of spatial data, such as the computational expense of spherical geometry or index bloat in high-write environments. This course provides advanced insights into the PostgreSQL 17 query planner and PostGIS 3.5 predicates that are not found in mainstream resources.
What You'll Build
You will build a production-grade "Geospatial Data Warehouse" capable of processing over a billion GPS pings per day. The system includes:
Ingestion Engine: Real-time streaming using Change Data Capture (CDC).
Spatial Storage: Declarative partitioning and Citus-based sharding.
Routing Engine: Optimized paths using pgRouting and Overture data.
Analytical Accelerator: Sub-second aggregations on multi-terabyte data using DuckDB.
Monitoring Dashboard: High-concurrency visualization using spatial clustering.
Who Should Take This Course?
This course is designed for Software Engineers, Architects, SREs, Data Engineers, and Product Managers who need to design resilient, location-aware systems at hyperscale.
What Makes This Course Different?
Unlike generic tutorials, this course focuses on "Day 2" operational realities: managing GiST index bloat, avoiding the "TOAST" trap, and navigating the trade-offs between H3 hexagons and S2 squares.
Key Topics Covered
PostgreSQL 17 internals for spatial joins.
Advanced indexing: GiST, SP-GiST, and BRIN.
Discrete Global Grids (H3 vs. S2).
Network Topology and Routing with pgRouting.
Scaling patterns: Partitioning, Sharding, and Redis Geo.
--Prerequisites
Proficiency in SQL and at least one backend language.
Basic familiarity with Docker and the Linux command line.
A "mental glossary" of terms like rasters, vectors, and SRIDs.
2. Course Structure & Curriculum (90 Lessons)
Module 1: Foundational Spatial Architecture and PostgreSQL 17
Learning Objective: Master spatial data types and the Architectural baseline of PostgreSQL 17.
1. Spatial Data Types in the 2025 Ecosystem.
2. PostgreSQL 17: Memory management for multi-terabyte warehouses.
3. PostGIS 3.5 Internal Mechanics: Spatial operator classes.
4. The Geometry vs. Geography Debate: Planar speed vs. spherical accuracy.
5. Spatial Reference Systems (SRID): Master 4326 vs. 3857.
6. Query Planner Improvements: Propagating column stats from CTEs.
7. Setting up the Warehouse Environment with Docker.
8. Importing Global Datasets: osm2pgsql vs. imposm3.
9. Standardizing IDs and Timestamps for global delivery.
10. Hands-on: Building your first high-scale spatial join.
Module 2: Elite Indexing and Optimization
Learning Objective: Optimize queries for petabyte-scale spatial logs using advanced indexing.
11. GiST (Generalized Search Tree) Deep Dive.
12. The "TOAST" Table Performance Trap.
13. Forcing the Planner: Diagnosing ignored indexes.
14. Caching Bounding Boxes for complex geometries.
15. SP-GiST for Uniform Point Data.
16. BRIN (Block Range Index) for massive append-only logs.
17. PostgreSQL 17 Parallel Index Creation.
18. Index Bloat: Why high-churn tables degrade performance.
19. Monitoring with pgstattuple.
20. REINDEX CONCURRENTLY: Maintenance without downtime.
Module 3: Discrete Global Grids - H3 vs. S2
Learning Objective: Implement grid-based indexing to replace expensive geometric joins.
21. The Grid Paradigm Shift: Joins on IDs, not geometry.
22. H3: Uber’s Hexagonal world view.
23. Why Hexagons? Equidistance and neighbor traversal.
24. S2: Google’s Hilbert Curve and quad-tree approach.
25. H3 vs. S2: Containment vs. Visualization.
26. Implementing H3 in PostGIS via h3-pg.
27. H3 Aggregation for Demand Heatmaps.
28. H3 Polyfill: Converting delivery zones to hexagonal sets.
29. A5 Pentagon Alternative for statistical analysis.
30. Choosing the Right Resolution for logistics matching.
Module 4: High-Performance Routing and Network Analysis
Learning Objective: Build a graph-based routing engine using pgRouting.
31. Introduction to pgRouting: Nodes and Edges.
32. Building the Topology: Vertex connectivity.
33. Conditioning Overture Transportation Data.
34. Dijkstra Algorithm at Scale.
35. A* and Heuristic Search: Speeding up pathfinding.
36. Traveling Salesperson Problem (TSP) for multi-stop delivery.
37. Dynamic Cost Updates: Live traffic integration.
38. Modeling Turn Restrictions and One-Way Streets.
39. Isochrones: Mapping 5-minute service areas.
40. Scaling pgRouting Memory for millions of edges.
Module 5: Advanced Geofencing and Dynamic Operations
Learning Objective: Design real-time logic for map-matching and geofence alerts.
41. Dynamic Geofencing with Voronoi Diagrams
42. ST_Subdivide: Cutting zones for faster point-in-polygon tests
43. Real-Time Map Matching: Snapping GPS to roads
44. Hidden Markov Models for trajectory reconstruction
45. Azimuth and Heading Analysis for directionality
46. Geofence Entry/Exit triggers at high concurrency
47. ST_Segmentize: Ensuring geodesic integrity
48. Geometric Simplification for mobile clients
49. Spatial Clustering: Grouping orders for driver batches
50. ST_DWithin: Why radius queries beat buffers
Module 6: Scaling to a Billion Pings
Learning Objective: Scale the warehouse horizontally using sharding and replication.
51. PostgreSQL 17 Declarative Partitioning: Time and Region
52. Partition-Wise Joins: v17 cross-shard optimizations
53. Citus: Distributed Postgres for petabyte spatial data
54. Shard Key Selection: Co-locating data by city_id
55. Read Replicas and Latency Lag Management
56. Redis Geo as a Proximity Cache
57. Connection Pooling with PgBouncer: 10k+ drivers
58. v17 Memory Tuning: shared_buffers and work_mem
59. WAL Compression for high-write GPS logs
60. High Availability with Patroni: Automated Failover
Module 7: Data Warehousing, ETL, and Analytical Acceleration
Learning Objective: Integrate columnar engines to achieve 1500x speedups.
61. Modern Spatial ETL with Airbyte
62. Change Data Capture (CDC) for real-time sync
63. DuckDB: The Analytical Power-Up for spatial rollups
64. pg_duckdb: Running DuckDB inside Postgres
65. GeoParquet: Storing historical data on S3
66. Building a Geospatial Data Lake
67. Handling Schema Drift in logistics metadata
68. Data Quality: ST_IsValid vs ST_MakeValid
69. Normalizing Spatial Metadata for restaurants
70. Exporting to BigQuery/Snowflake via ogr2ogr
Module 8: SRE for PostGIS - Monitoring and Maintenance
Learning Objective: Maintain 24/7 reliability and performance in production.
71. Monitoring GiST Index Bloat: Automated detection.
72. Autovacuum Tuning for high-write tables.
73. v17 Adaptive Vacuuming: Smarter cleanup thresholds.
74. Managing Transaction ID Wraparound.
75. Failover Slots in v17: Seamless replication recovery.
76. Benchmarking PostGIS vs. Presto for big queries.
77. Checkpoint Configuration for tracking stability.
78. Cache Hit Ratio: Keeping indexes in RAM.
79. PostgreSQL 18 Preview: Asynchronous I/O (AIO).
80. The Maintenance Checklist for Spatial DBAs.
Module 9: Product Management, UI/UX, and Capstone
Learning Objective: Bridge technical constraints with business and user needs.
81. PM’s Guide to Spatial Trade-offs: Accuracy vs. Cost.
82. Latency Budgeting for real-time driver tracking.
83. Map Clutter: Designing clustering for 10k+ pins.
84. Semantic Color and Dashboard Hierarchy.
85. Progressive Disclosure in Map interfaces.
86. The "Map-First" Fallacy: When maps aren't the answer.
87. Capstone: Designing the Billion-Ping Schema.
88. Capstone: Implementing the Scaled Infrastructure.
89. Capstone: The Load Test - 1.2M Queries Per Second.
90. Capstone: Final Production-Ready Delivery.